Optomechanical parts are the unsung heroes of optical systems, ensuring precise alignment, stability, and protection for delicate components like lenses, mirrors, and detectors. From the housing that shields a laser from dust to the tiny screw that fine-tunes a microscope’s focus, each part plays a critical role in achieving the desired optical performance. In this guide, we’ll explore the diverse world of optomechanical components, providing explanations, images, and design tips to help you understand their functions and importance.
Optical Housing
Optical Housings are precision-engineered enclosures that securely hold and protect optical components like lenses and mirrors. They maintain exact alignment and safeguard optics from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and mechanical stress. High precision is critical, as even the slightest misalignment can affect the optical system’s performance. These housings are typically made from durable materials like aluminum or stainless steel to ensure long-term stability and reliability in sensitive applications like cameras, lasers, and scientific instruments.

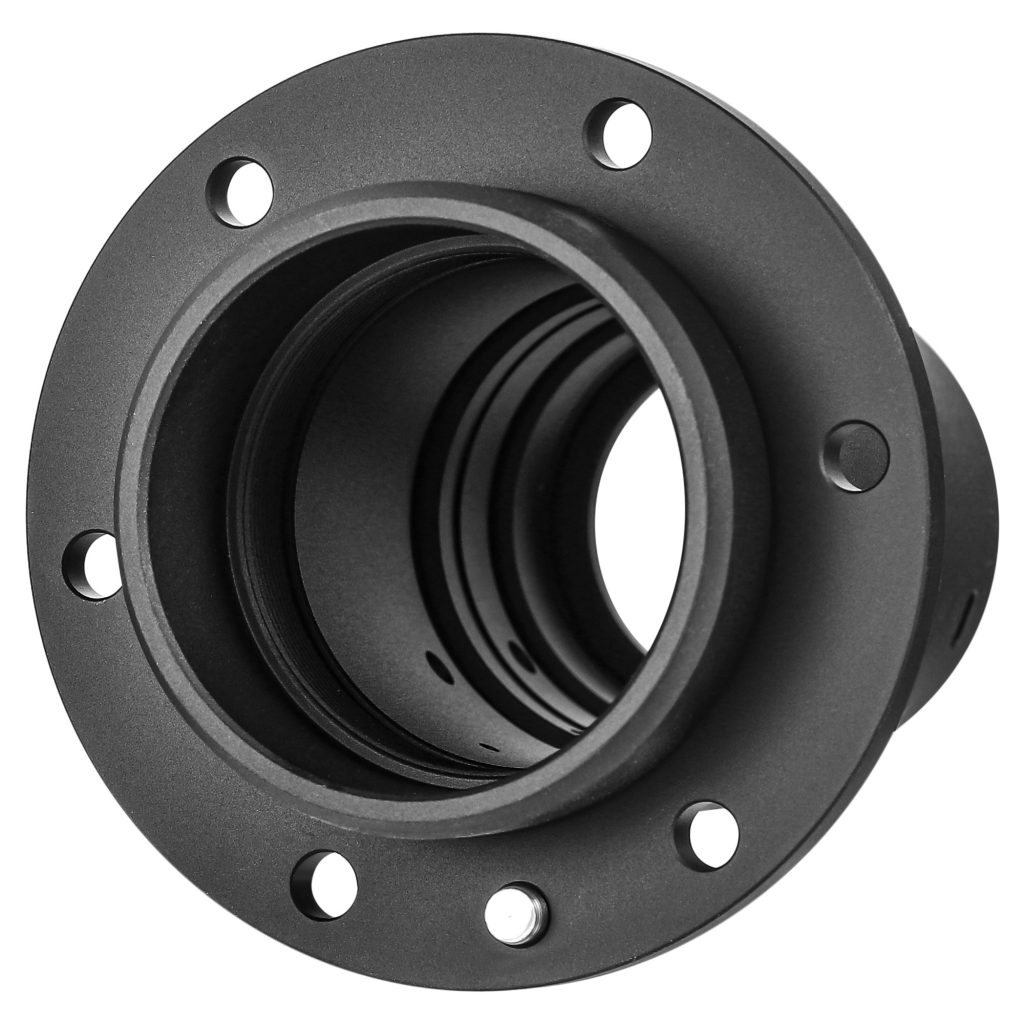
Spectrometer Housing
A spectrometer housing is a critical component in optical systems, safeguarding delicate spectrometer parts like diffraction gratings and detectors. These housings provide a stable, protected environment, shielding the spectrometer from dust, moisture, temperature fluctuations, and vibrations that can interfere with accurate measurements. The accuracy of the housing’s machining directly impacts the spectrometer’s performance, ensuring precise alignment and reliable spectral analysis. This specific housing features a sand-blasted matte finish to minimize internal reflections and stray light, further optimizing its performance.
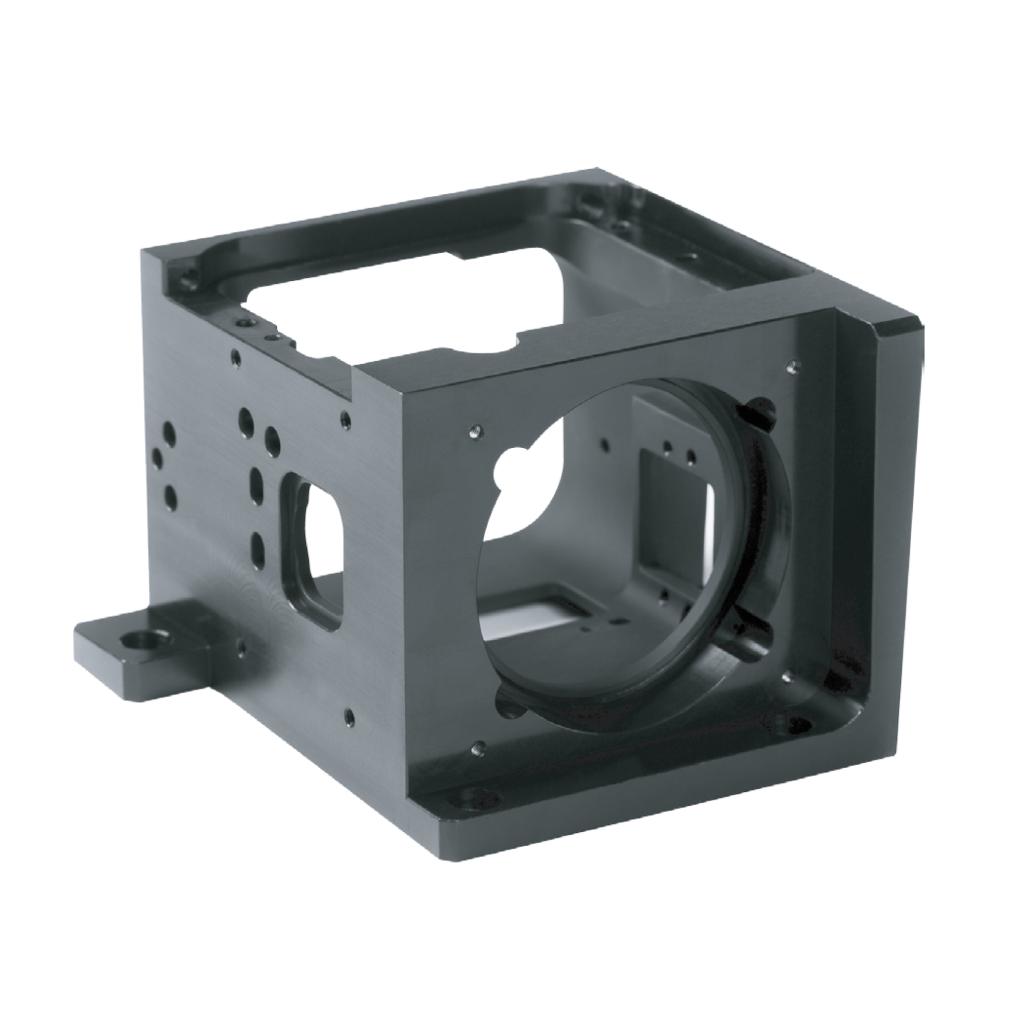

Static Lens Mount
Static lens mount are precision components used to securely hold and align optical lenses in optical applications to direct and route light beams from their source to a target area. They are essential for precise beam alignment in various industries, including research, biomedical, life sciences, astronomy, metrology, and semiconductor manufacturing. These mounts need to be highly precise for accurate positioning on the plate or housing.
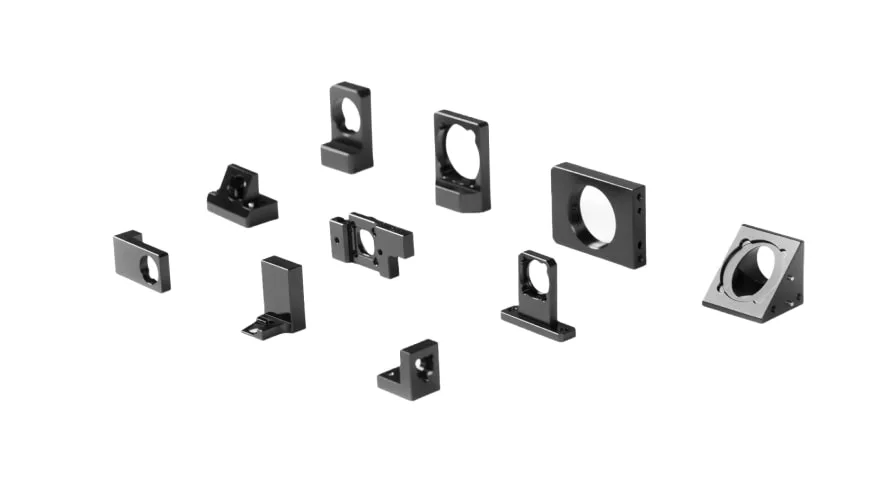

Adjustment Screws
Adjustment screws are essential optomechanical component, providing precise and controlled movement for aligning optical elements with high accuracy. These screws typically feature fine threads, specifically designed for optical adjustments, enabling minute positional changes that are critical for optimizing optical systems. They can be sourced from standard optomechanical component manufacturers like Thorlabs and then modified if necessary, or they can be custom-produced from scratch to meet specific application requirements. Often crafted from durable stainless steel with brass sleeves, these adjustment screws offer a balance of strength, stability, and smooth movement, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliable optical alignment in demanding applications.
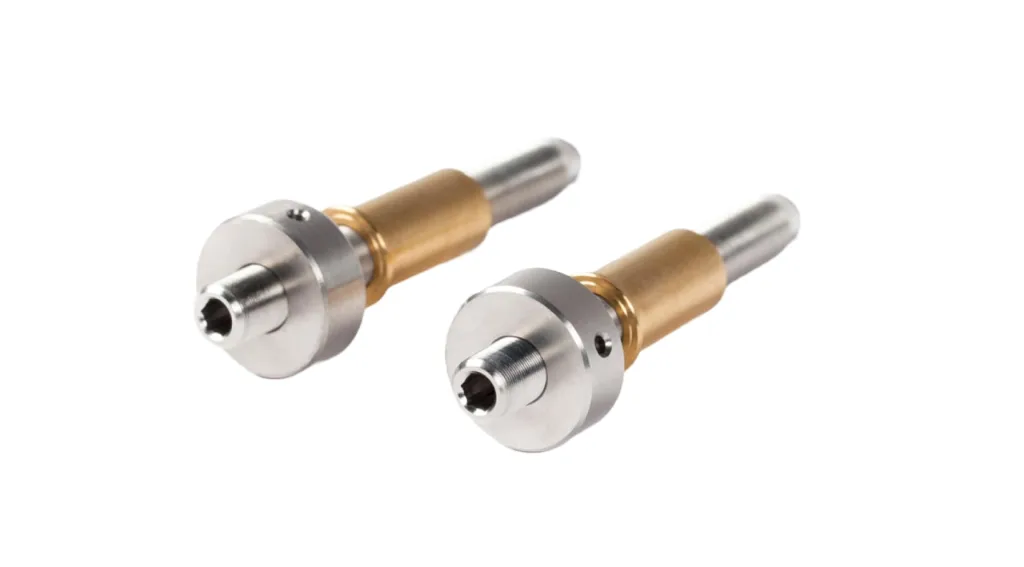

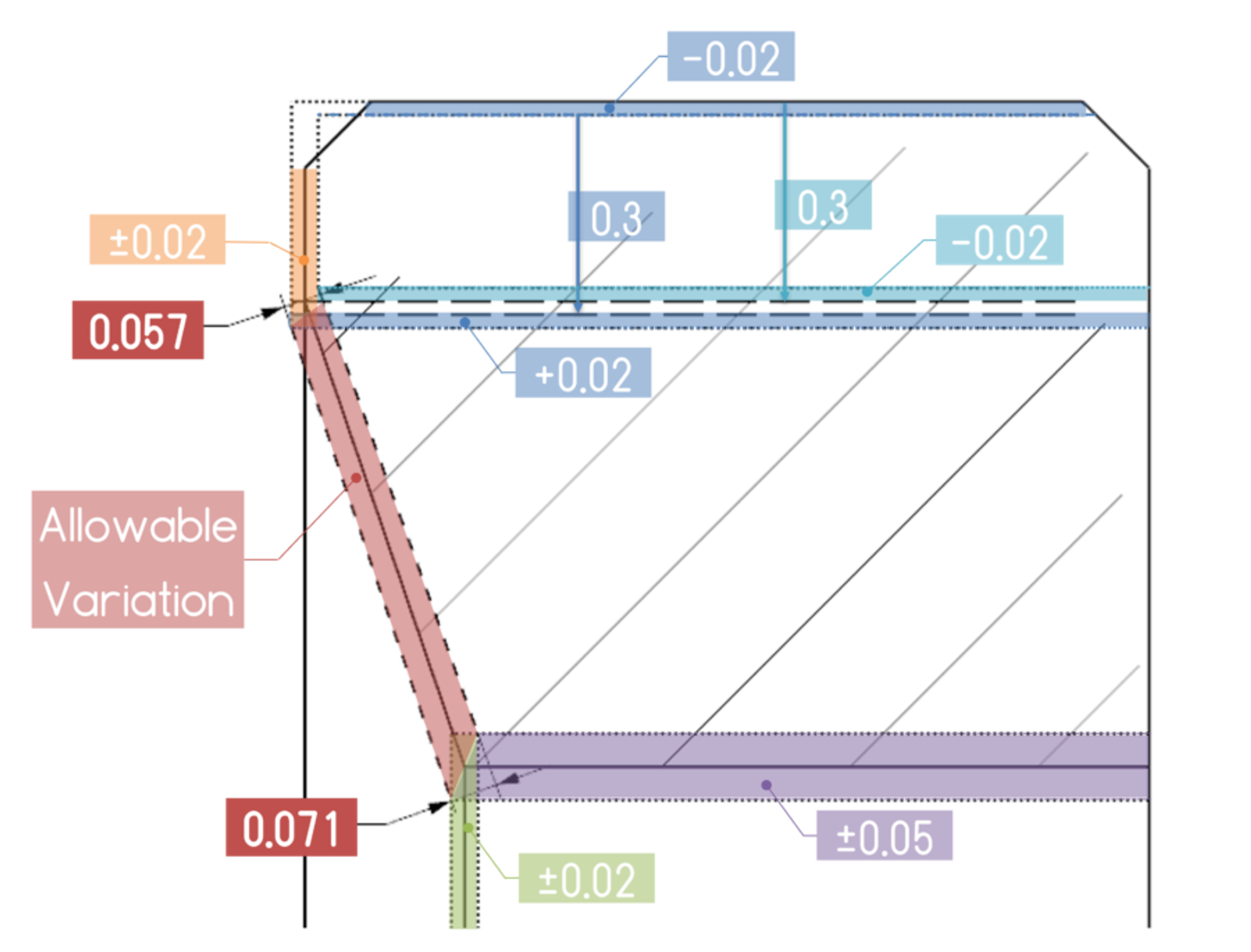
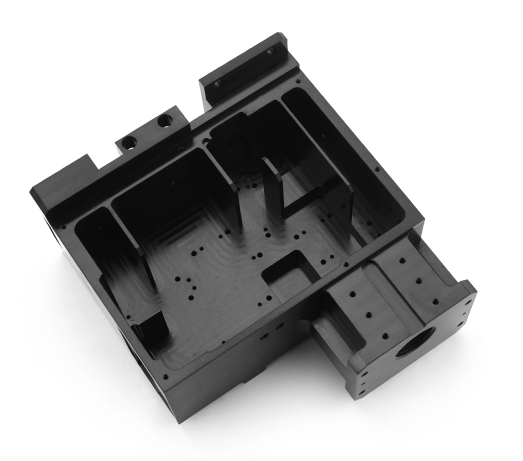
Base Plates
Custom optical systems base plates are the foundation upon which precision optical systems are built. These plates, typically crafted from aluminum or aluminum-based alloys like C250 or ACP5080, provide a stable and reliable platform for mounting various optomechanical parts. Dimensional stability is paramount, as even slight variations can impact the accuracy and performance of the optical system. To ensure this stability, the material is often stress-relieved to minimize dimensional changes over time. The flatness of the mounting surfaces and the precision location of the pins or pin holes on the plate are critical, directly influencing the precise positioning and alignment of optical components, and therefore the overall performance and reliability of the optical system.
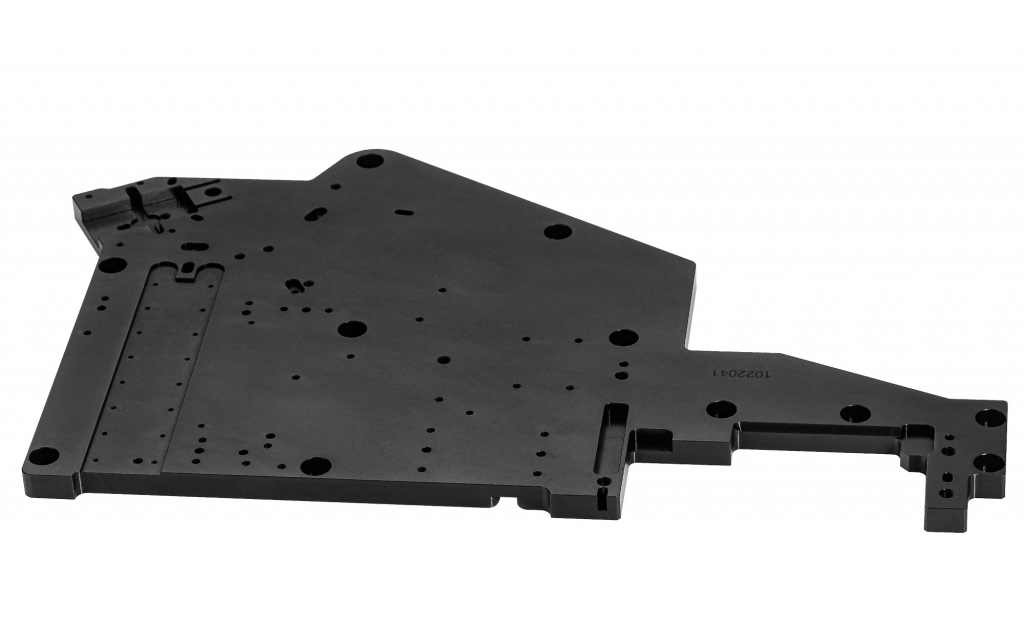
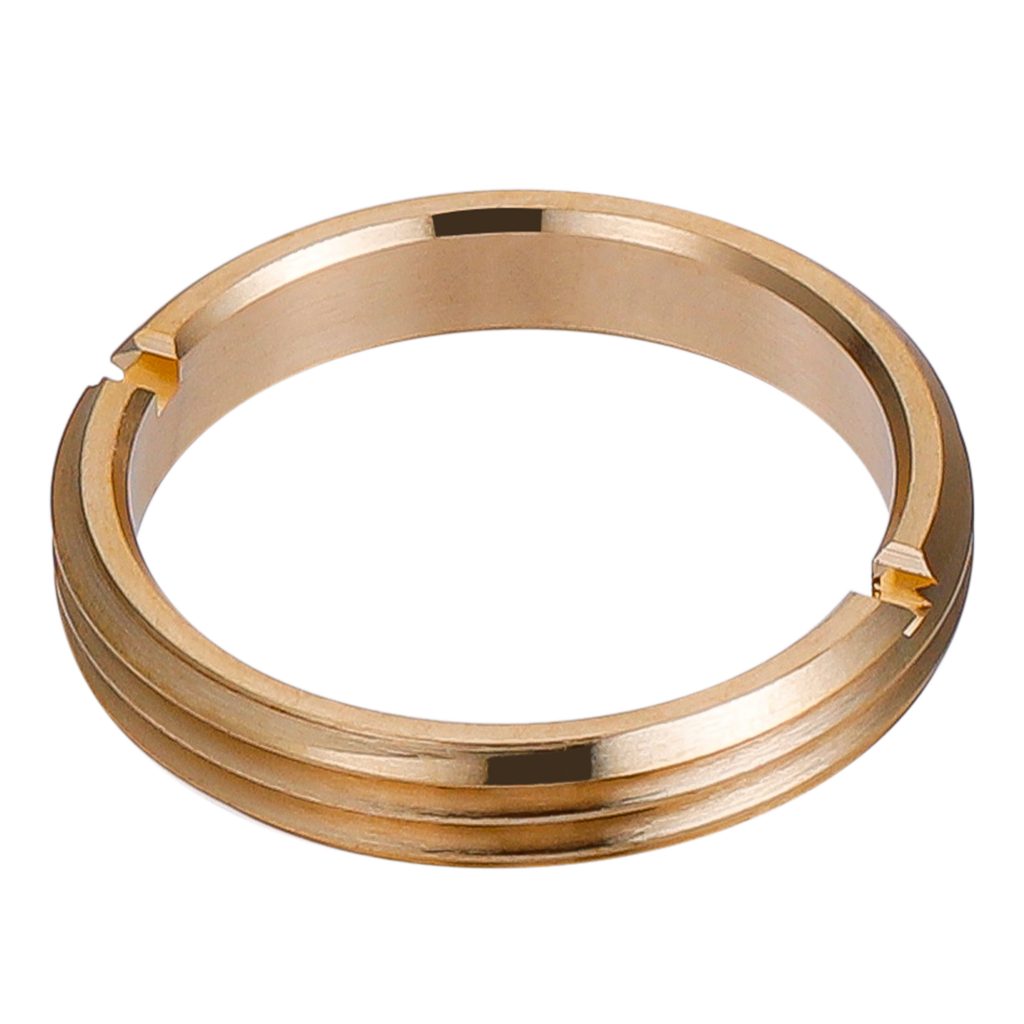
Retainers
Retainers are essential in Optomechanics for securely holding and precisely positioning optical components like lenses and mirrors within their mounts. This secure hold prevents movement or misalignment that could degrade the optical system’s performance. Commonly used in optical barrels, condenser housings, and other assemblies, retainers usually “push” the optical element against a precisely machined surface within an accurate diameter, which together determine the element’s position relative to other optical components. Brass is often chosen for retainers due to its combination of strength and slight flexibility. This allows for minute adjustments during temperature changes, preventing stress on the delicate optic, which is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and long-term reliability.

Practical tips:
Filter Wheels
Filter wheels are mechanical devices used to hold and rotate optical filters in front of light sources or detectors. They are commonly used in imaging and spectroscopy systems to switch between different filters, allowing the user to selectively transmit specific wavelengths of light. Filter wheels are often motorized, enabling precise and automated control over which filter is placed in the optical path. They are critical in applications like fluorescence microscopy, astronomy and machine vision, where different wavelengths or colors need to be isolated for analysis or imaging.
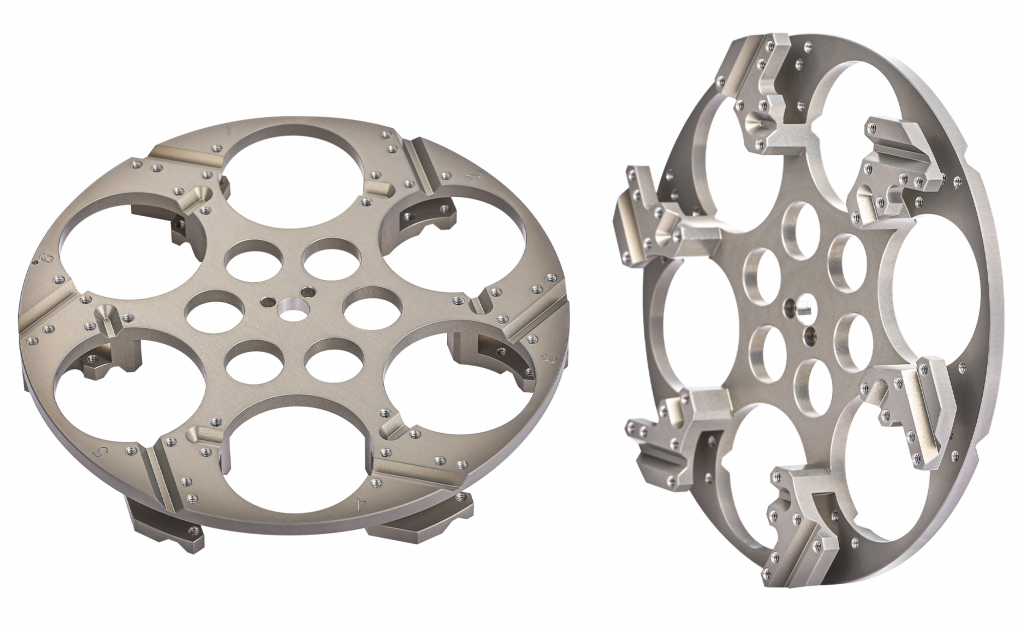
Condenser housing
A condenser housing is a crucial component in optical systems, specifically designed to house and protect the condenser lens. This housing ensures the condenser lens is held securely in the correct position and alignment, which is vital for controlling and concentrating light onto the object being viewed. The precise positioning of the condenser lens within its housing directly influences the quality and uniformity of illumination, affecting the overall performance of the optical system.